---
title: Fauna and Fly.io
layout: docs
sitemap: false
nav: firecracker
categories:
- database
---
[Fauna](https://fauna.com/+external) is a distributed relational database with a document data model, and delivered as an API. Databases created in Fauna automatically get three geographically distributed replicas with active-active writes and ACID compliance, making it a powerful complement to Fly.io in serving low latency reads and writes for dynamic global applications.
## Starter kit
Fauna provides [starter kits](https://github.com/orgs/fauna-labs/repositories?q=fly-io-starter+external) to help you quickly launch an app on Fly.io, using Fauna as the database backend. Before you start, read the short section below to learn how Fauna and Fly.io makes for a great combination when building low latency, dynamic global applications.
## Region Groups
A Fauna Region Group refers to the locality footprint of where the replicas are located, and allows you to control where your data resides, making it possible to comply with data locality legislation, such as the General Data Protection Regulation ([GDPR](https://gdpr-info.eu/+external)).
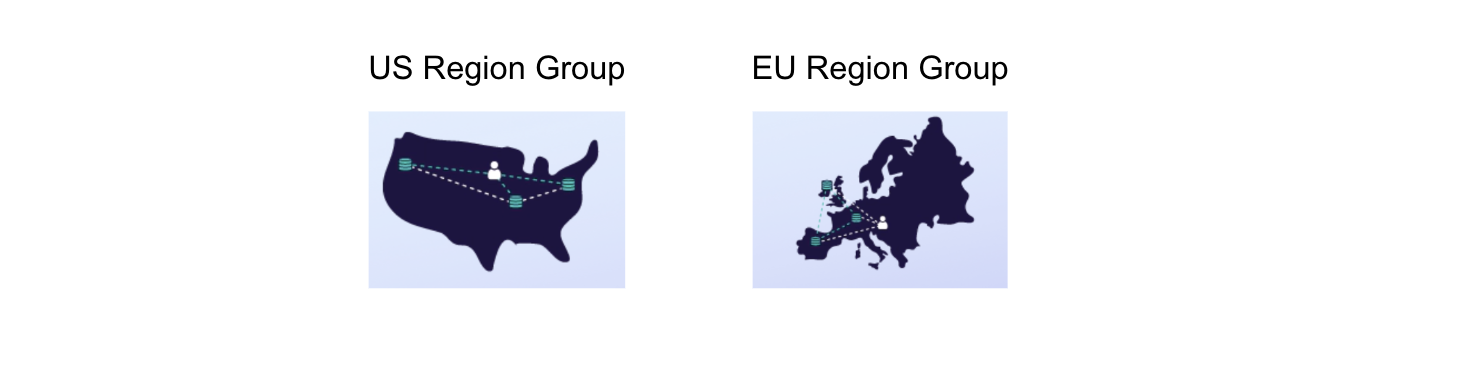
When you create a database in Fauna, you choose which Region Group you want the database created in. When you query the database, your request is automatically routed to the closest replica (within the Region Group) based on latency. This functionality comes out-of-the-box without any special configuration or deployment strategy.
## Scale your deployment to match the Fauna footprint
Currently, Fauna provides 2 choices of Regions Groups, US and EU. The table below lists the Fly.io regions that are closest to the Fauna replicas of each respective Region Group:
| Fauna Region Group | Deploy on Fly Regions |
|--------------------|-----------------------|
| EU | lhr, arn, fra |
| US | sjc, ord, iad |
To take full advantage of Fauna's distributed footprint, you should deploy your app on 3 Fly.io regions as well, and as close as possible to the Region Groups' replicas.
For example, let's say you created your Fauna database in the US Region Group and you used the Fauna [Python Fly.io starter kit](https://github.com/fauna-labs/python-fly-io-starter+external) with the default configuration to create your Fly app. Your app will be in the `sjc` region, as determined by `primary_region` in the `fly.toml` config file. You can add Machines in the other closest US regions using this command:
```
fly scale count 2 --region ord,iad
```
Run `fly scale show` to see where your app's Machines are running. For example:
```cmd
fly scale show
```
```output
VM Resources for app: my-app-name
Groups
NAME COUNT KIND CPUS MEMORY REGIONS
app 3 shared 1 256 MB iad,ord,sjc
```
Fauna and Fly.io
Fauna is a distributed relational database with a document data model, and delivered as an API. Databases created in Fauna automatically get three geographically distributed replicas with active-active writes and ACID compliance, making it a powerful complement to Fly.io in serving low latency reads and writes for dynamic global applications.
Starter kit
Fauna provides starter kits to help you quickly launch an app on Fly.io, using Fauna as the database backend. Before you start, read the short section below to learn how Fauna and Fly.io makes for a great combination when building low latency, dynamic global applications.
Region Groups
A Fauna Region Group refers to the locality footprint of where the replicas are located, and allows you to control where your data resides, making it possible to comply with data locality legislation, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
When you create a database in Fauna, you choose which Region Group you want the database created in. When you query the database, your request is automatically routed to the closest replica (within the Region Group) based on latency. This functionality comes out-of-the-box without any special configuration or deployment strategy.
Scale your deployment to match the Fauna footprint
Currently, Fauna provides 2 choices of Regions Groups, US and EU. The table below lists the Fly.io regions that are closest to the Fauna replicas of each respective Region Group:
Fauna Region Group
Deploy on Fly Regions
EU
lhr, arn, fra
US
sjc, ord, iad
To take full advantage of Fauna’s distributed footprint, you should deploy your app on 3 Fly.io regions as well, and as close as possible to the Region Groups’ replicas.
For example, let’s say you created your Fauna database in the US Region Group and you used the Fauna Python Fly.io starter kit with the default configuration to create your Fly app. Your app will be in the sjc region, as determined by primary_region in the fly.toml config file. You can add Machines in the other closest US regions using this command:
fly scale count 2 --region ord,iad
Run fly scale show to see where your app’s Machines are running. For example:
fly scale show
VM Resources for app: my-app-name
Groups
NAME COUNT KIND CPUS MEMORY REGIONS
app 3 shared 1 256 MB iad,ord,sjc